
PTSD is a common mental issue in individuals who have encountered or seen a horrendous mishap, for example, a catastrophic event, a severe accident, a terrorist act, war/battle, or rape or who have been threatened with death, sexual viciousness or severe injury.
PTSD has been known by many names previously, for example, “shell shock” during WWI and “combat fatigue” after WWII; however, PTSD doesn’t simply end up combatting veterans. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder can happen in all people of any identity, ethnicity or culture, and age.
How Common is PTSD?
Around 50% of individuals in the United States have encountered a traumatic accident. Among this group, 10% of men and 20% of women foster Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in the Real Society. Ladies experience neglect or abuse during childhood more frequently than men. They additionally experience rape and aggressive behavior at home more regularly. Ladies will generally encounter trauma uniquely in contrast to men, as well.
Concept of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
In the initial weeks and days after a horrendous accident, individuals frequently experience heightened arousal, sharpness, searching for risk and being on guard. These responses often substitute with deadness and separation. It likewise brings consistent recollections of the events and felt it might reoccur. It additionally evokes overwhelming inclinations of dread, misery, responsibility, outrage, or pain. Generally, these responses and sentiments will determine all alone throughout the next couple of weeks; nonetheless, if the reactions and pain proceed, it might imply that the individual is in danger of creating PTSD or another mental health condition.
Anybody can foster PTSD following a traumatic event; however, individuals are at greater risk if:
- The event included physical or rape
- They encountered serious helplessness
- The event included something they never suspected would happen to them
- They have had other horrible experiences implying vulnerability or risk, including physical or sexual maltreatment, fender benders, criminal events, cataclysmic events or struggle
- They have experienced Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder previously.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of PTSD?
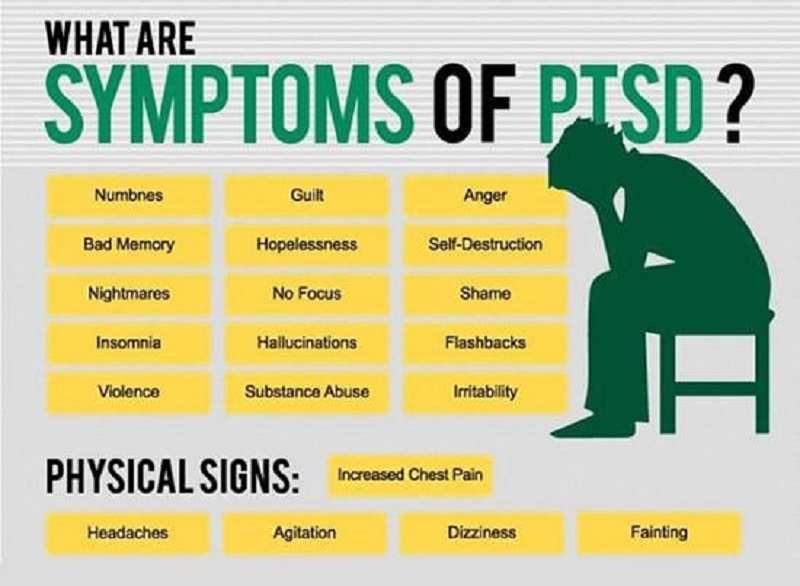
Most children and adolescents with PTSD will:
- People have disturbing considerations about the injury.
- They have terrible dreams or sleep issues
- Individuals have terrible memories, called flashbacks, that make it seem like the injury is as yet occurring.
- Individuals avoid things that help them to remember the injury.
- Be more effortlessly alarmed, frightened, or restless.
- Feel more moody, miserable, irate, or not appreciate things as in the past.
- Try not to remember a few pieces of what occurred
More youthful kids might show more unfortunate and regressive behaviours. They may re-establish the injury through play.
When side effects like these occur in the first days and weeks after the trauma, it could be called an intense stress reaction. Specialists analyze PTSD when side effects last longer than a month.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Children and Teenagers
Older kids and young people experience similar issues to grown-ups when they foster PTSD. More youthful kids can communicate trouble in different ways. For instance, they may re-experience the horrendous mishap through repetitive play instead of having undesirable remembers of the event during the day. Numerous kids have terrifying dreams without conspicuous content instead of bad dreams that replay the awful mishap. Kids may likewise lose interest in play, become socially removed, or have outrageous temper tantrums.
Around 33% of children who experience a horrible accident will foster PTSD.
Different issues that can create close by PTSD include nervousness or sadness, disobedient way of behaving, consideration deficiency, hyperactivity jumble, and in youngsters and young adults, suicidal thoughts and liquor or medication use.
When to Get Medical Advice
It’s generally expected to encounter disturbing and confounding considerations after a horrible accident; however, the vast majority work on usually more than half a month.
You should see a doctor if you or your child are having issues around a month after the horrendous experience or if the side effects are exceptionally inconvenient.
If necessary, your GP can allude to psychological well-being experts for additional evaluation and treatment.
How Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is Treated
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder can be treated effectively, even when it creates numerous years after a horrendous accident.
Any treatment relies upon the seriousness of side effects and how soon they happen after the horrendous accident.
Any of the accompanying treatment choices might be suggested:
Watchful Waiting – Checking your side effects to see whether they improve or seek more regrettable without treatment.
Antidepressants – Such as mirtazapine or paroxetine.
Psychological Therapies – Examples include eye movement desensitization or trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy and reprocessing.
How Does Therapy Help?
Trauma therapy gives kids an approach to securely discuss their thoughts, recount their stories, and get support.
In therapy, kids master adapting and quieting abilities to assist them with managing the uneasiness they feel after a trauma. This makes it simpler to discuss what they’ve experienced.
Through therapy, kids figure out how to change a portion of their viewpoints about the injury. They figure out how to relinquish any culpability or disgrace about what has happened to them. Gradually, they figure out how to confront things they used to avoid.
PTSD Therapy assists kids with acquiring fortitude and certainty. Kids utilize their assets to adapt.
So, you can allude yourself straightforwardly to a mental therapies service.
